-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Cryptography
Cryptography is a method of storing and transmitting data in a particular form so that only those for whom it is intended can read and process it. cryptography is most often associated with scrambling plaintext (ordinary text, sometimes referred to as cleartext) into ciphertext (a process called encryption), then back again (known as decryption). Individuals who practice this field are known as cryptographers.
Modern cryptography concerns itself with the following four objectives:
- Confidentiality (the information cannot be understood by anyone for whom it was unintended)
- Integrity (the information cannot be altered in storage or transit between sender and intended receiver without the alteration being detected)
- Non-repudiation (the creator/sender of the information cannot deny at a later stage his or her intentions in the creation or transmission of the information)
- Authentication (the sender and receiver can confirm each other?s identity and the origin/destination of the information)
Cryptography Terms:
Encryption: It is the process of locking up information using cryptography. Information that has been locked this way is encrypted.
Decryption: The process of unlocking the encrypted information using cryptographic techniques.
Key: A secret like a password used to encrypt and decrypt information. There are a few different types of keys used in cryptography.
Symmetrical Encryption
This is the simplest kind of encryption that involves only one secret key to cipher and decipher information. Symmetrical encryption is an old and best-known technique. It uses a secret key that can either be a number, a word or a string of random letters. It is a blended with the plain text of a message to change the content in a particular way. The sender and the recipient should know the secret key that is used to encrypt and decrypt all the messages. Blowfish, AES, RC4, DES, RC5, and RC6 are examples of symmetric encryption. The most widely used symmetric algorithm is AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256.
The main disadvantage of the symmetric key encryption is that all parties involved have to exchange the key used to encrypt the data before they can decrypt it.

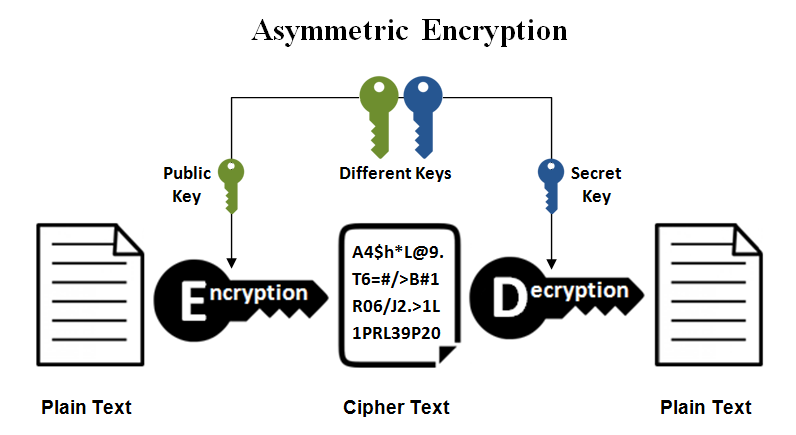
Asymmetrical Encryption
Asymmetrical encryption is also known as public key cryptography, which is a relatively new method, compared to symmetric encryption. Asymmetric encryption uses two keys to encrypt a plain text. Secret keys are exchanged over the Internet or a large network. It ensures that malicious persons do not misuse the keys. It is important to note that anyone with a secret key can decrypt the message and this is why asymmetrical encryption uses two related keys to boosting security. A public key is made freely available to anyone who might want to send you a message. The second private key is kept a secret so that you can only know.
A message that is encrypted using a public key can only be decrypted using a private key, while also, a message encrypted using a private key can be decrypted using a public key. Security of the public key is not required because it is publicly available and can be passed over the internet. Asymmetric key has a far better power in ensuring the security of information transmitted during communication.